Reduction of graphene oxide – a comprehensive electrochemical investigation in alkaline and acidic electrolytes†
Abstract
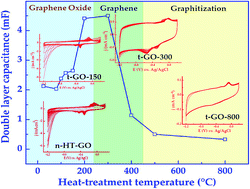
Graphene synthesized by the reduction of graphene oxide (GO) features in a myriad of applications ranging from sensors to batteries and catalysts to dye-sensitized solar cells. The exceptional physical and electrochemical properties of graphene originate from the presence of several residual functional groups and the non-stoichiometry in its structure. But, investigating the evolution of graphene from GO has been a daunting task. In this manuscript, simple electrochemical methods are reported to characterize GO subjected to thermal, electrochemical, and chemical reduction. The electrochemical features of these samples along with their FTIR spectra and XRD patterns help to identify the functional groups and provide compelling evidence for the transformation among them during the reduction of GO. The redox features of the voltammograms suggest the conversion of epoxides to carbonyl, carbonyl to carboxylic acid groups, and their subsequent removal with potential cycling. Thermal treatment of GO in the range of 80–150 °C causes the conversion of some of the epoxides to carbonyls and removal of water content. At the same time, epoxides are more prevalent in chemically reduced GO. The double layer capacitance – one of the figure of merits that distinguishes graphene from other carbon allotropes – gives an indication of the reduced graphene oxide content in the sample. Thus, electrochemical characterization sheds significant light onto the nature of oxygen moieties in non-heat-treated GO (n-HT-GO), thermally reduced GO (t-GO), chemically reduced GO (c-RGO) and electrochemically reduced GO (e-RGO), besides explaining the range of reported electrochemical capacitance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...