In vitro and in vivo evaluation of Rapamycin-eluting nanofibers coated on cardia stents
Abstract
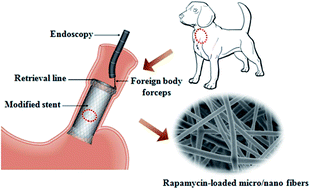
It is known that a Rapamycin (Rapa)-coating on stents can be potentially applied to treat benign cardia stricture, it is, however, difficult to use as a delivery system for controlled and sustained release particularly in an acidic environment. The aim of this study was therefore to explore the potential of self-expandable metal stents covered with Rapa-loaded electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fiber membranes for controlled Rapa delivery to inhibit inflammation and tissue hyperplasia. It was found that stents coated with the membranes had comparable mechanical properties including expansion properties, mechanical strength and rigidity with bare cardia stents. In addition, Rapa was found to be released from the membrane coated stents in a controlled and sustained manner, and via varying the concentration of Rapa incorporated in the PCL membranes, the drug release rates could be controlled. The released Rapa was also found to inhibit the proliferation of smooth muscle cells. Moreover, the site implanted with the stents coated with the Rapa loaded PCL membranes showed reduced tissue inflammation and collagen fiber deposition compared to those with no coating. The above results have therefore suggested that the new Rapa-coated stents developed in this study have great potential to treat benign cardia strictures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...