Understanding the photothermal effect of gold nanostars and nanorods for biomedical applications
Abstract
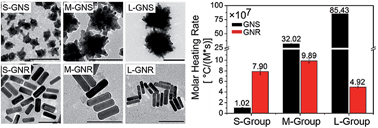
The plasmon-based photothermal effect of gold nanorod (GNR) has undergone the most systematic investigation for cancer therapy in the biomedical realm. In recent years, gold nanostar (GNS) has come into sight with its attractive ability to transduce electromagnetic radiation into heat. Understanding photothermal conversion efficiency is thus becoming more important for the selection of suitable materials for photothermal therapy. In this article, we investigated systematically the photothermal conversion efficiency and the molar heating rate of GNS and GNR in three groups (S-group, M-group and L-group, representing groups of nanostructures with central extinctions at shorter, medium and longer wavelengths, respectively), to better understand the behaviour of GNS and GNR in the field of photothermal therapy. In the M-group and L-group, the photothermal conversion efficiencies of GNSs and GNRs are similar, while GNSs have a much higher molar heating rate than GNRs. Among all the samples, L-GNS has the highest molar heating rate, because of its large molar extinction coefficient. In addition, the discrete dipole approximation (DDA) was employed to simulate the optical properties of gold nanoparticles with different shapes, and the photothermal properties of GNSs and GNRs were compared experimentally and theoretically. From both the experimental and the theoretical results, M-GNS and L-GNS exhibit higher extinction efficiencies than M-GNR and L-GNR, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...