Optically and magnetically doped ormosil nanoparticles for bioimaging: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro studies†
Abstract
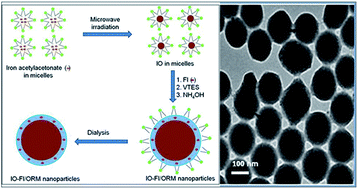
In this manuscript, we report the fabrication of a dual-modality nanoprobe involving the co-encapsulation of fluorophores and iron oxide nanoparticles within ormosil nanoparticles, and their applications in in vitro bioimaging. The entire synthesis, including microwave-mediated precipitation of the iron oxide nanoparticles, was carried out within the non-aqueous core of an oil-in-water microemulsion. The nanoparticles are spherical and monodispersed, with an average diameter of around 150 nm. After synthesis, their composition, stability, crystallinity, as well as their magnetic and optical properties were evaluated. X-ray diffraction studies of the non-encapsulated iron oxide nanoparticles showed them to be crystalline, corresponding to an α-Fe2O3 phase. However, their crystallinity was found to diminish upon ormosil encapsulation. These doped nanoparticles displayed both optical and superparamagnetic properties, by virtue of which they have the potential to serve as dual diagnostic probes. The stability of the fluorophores was found to increase upon nanoencapsulation. In vitro studies have shown that the nanoparticles are non-toxic to cells in culture and undergo efficient cellular uptake, as shown by optical bioimaging. These observations demonstrate the promise of such nanoparticles for non-toxic bioimaging applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...