Structural evolution from TiO2 nanoparticles to nanosheets and their photocatalytic performance in hydrogen generation and environmental pollution removal†
Abstract
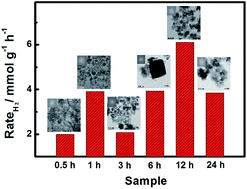
The rapid depletion of the fossil fuel reserves, and the increase of green-house gas emissions and other environmental pollutants, bring up an urgent need for the development of clean energy and sustainable environmental solutions. The ability to use sunlight to produce fuels such as H2 from abundant, non-toxic resources, and to decompose environmental pollutants with benign photocatalysts, would revolutionize our civilization. TiO2 has attracted substantial interest due to its activity for generating hydrogen from water under ultraviolet (UV) light irradiation. The discovery of (001) facet control with the fluoride additive in the reactants has triggered intensive studies for model photocatalysis. Here, we found that small TiO2 nanoparticles were formed at the very beginning stage of the reaction, then were transformed into large TiOF2 crystals, and finally turned into (001)-faceted TiO2 nanosheets. TiOF2 acted as a metastable intermediate medium in the transformation from TiO2 nanoparticles into (001)-faceted TiO2 nanosheets. The (001) face showed higher activity for the photocatalytic generation of hydrogen and the photodecomposition of methylene blue and rhodamine B. The synergic effect between TiOF2 and TiO2 nanosheets or nanoparticles further improved the photocatalytic activities. This study provides us with a promising solution for solving the energy and environment problems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...