Galactosylated biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone-co-phosphoester) random copolymer nanoparticles for potent hepatoma-targeting delivery of doxorubicin
Abstract
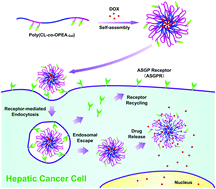
A novel galactosamine (Gal)-mediated drug delivery carrier, Gal-conjugated biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone-co-phosphoester) random copolymer [poly(CL-co-OPEA-Gal)], was developed for enhanced hepatoma-targeting delivery of anti-cancer drug doxorubicin (DOX). The functionalized copolymers were synthesized via a combination of ring-opening polymerization (ROP), photoinduced thiol–ene reaction and amidation reaction. The chemical composition and structures, as well as the molecular weights and molecular weight distributions of these copolymers, were characterized by 1H NMR, 31P NMR and GPC analyses. Morphological study indicated that all the poly(CL-co-OPEA-Gal) nanoparticles (Gal-NPs), DOX-loaded nanoparticles (DOX/Gal-NPs), pristine polymeric nanoparticles without Gal modification (NPs) and DOX-loaded nanoparticles without Gal modification (DOX/NPs) displayed a spherical shape with averaged diameters below 200 nm. The in vitro drug release behavior of DOX/Gal-NPs was featured with a pH-dependent manner due to the degradable components of the random copolymer sensitive to the environmental stimuli. Cellular uptake studies demonstrated that DOX/Gal-NPs can be internalized into HepG2 cells more efficiently compared with HeLa cells owing to specific ligand–receptor interactions between Gal and asialoglycoprotein receptors (ASGPRs) on the surface of HepG2 cells. In vitro cytotoxicity tested by the MTT assay indicated that these random copolymers showed favorable biocompatibility. DOX/Gal-NPs exhibited a higher antitumor efficacy than DOX/NPs against HepG2 cells. These results show that these biodegradable Gal-decorated poly(CL-co-OPEA-Gal) nanoparticles are highly promising for targeted delivery of water-insoluble anti-cancer drugs for hepatocellular carcinoma.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...