Photocatalytic degradation of pentachlorophenol by N–F–TiO2: identification of intermediates, mechanism involved, genotoxicity and ecotoxicity evaluation†
Abstract
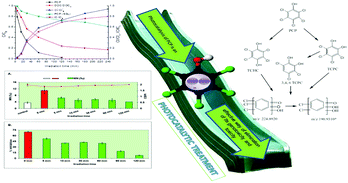
In the present study the photocatalytic degradation of a toxic priority pollutant, PCP, in the presence of N–F codoped TiO2 was explicitly investigated. The efficiency of the process to remove PCP was monitored for the first time through combined evaluation of several aspects: the kinetic study of the PCP degradation, identification of transformation products by a combination of mass spectrometric techniques (HR-LC-MS and GC-MS), assessment of total mineralization during the process, and evaluation of the genotoxicity and ecotoxicity of the initial and treated solutions applying the cytokinesis block micronucleus (CBMN) assay and Microtox assay, respectively. On the basis of identified products, a proposed degradation pathway is presented, involving mainly oxidative dechlorination reactions. Genotoxicity and ecotoxicity studies clearly demonstrated the efficiency of the photocatalytic process in the detoxification as well as in the elimination of genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of the irradiated solutions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Solar Chemistry and Photocatalysis - environmental applications

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...