The study of polyplex formation and stability by time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy of SYBR Green I-stained DNA
Abstract
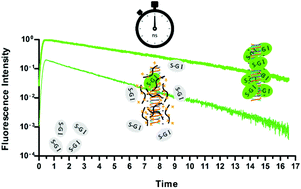
Polyplexes are nanoparticles formed by the self-assembly of DNA/RNA and cationic polymers specifically designed to deliver exogenous genetic material to cells by a process called transfection. There is a general consensus that a subtle balance between sufficient extracellular protection and intracellular release of nucleic acids is a key factor for successful gene delivery. Therefore, there is a strong need to develop suitable tools and techniques for enabling the monitoring of the stability of polyplexes in the biological environment they face during transfection. In this work we propose time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy in combination with SYBR Green I-DNA dye as a reliable tool for the in-depth characterization of the DNA/vector complexation state. As a proof of concept, we provide essential information on the assembly and disassembly of complexes formed between DNA and each of three cationic polymers, namely a novel promising chitosan-graft-branched polyethylenimine copolymer (Chi-g-bPEI), one of its building block 2 kDa bPEI and the gold standard transfectant 25 kDa bPEI. Our results highlight the higher information content provided by the time-resolved studies of SYBR Green I/DNA, as compared to conventional steady state measurements of ethidium bromide/DNA that enabled us to draw relationships among fluorescence lifetime, polyplex structural changes and transfection efficiency.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...