New cyclometallated Ru(ii) complex for potential application in photochemotherapy?†
Abstract
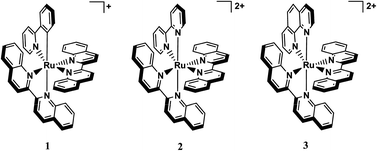
In an effort to create a molecule that absorbs further into the optimum window for photochemotherapy (PCT), the new cyclometallated complex [Ru(biq)2(phpy)](PF6) (1, biq = 2,2′-biquinoline, phpy− = deprotonated 2-phenylpyridine) was synthesized, characterized and compared to the known photoactive complexes [Ru(biq)2(bpy)](PF6)2 (2, bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine) and [Ru(biq)2(phen)](PF6)2 (3, phen = 1,10-phenanthroline), both of which undergo exchange of one biq ligand when irradiated with red light in coordinating solvents. Excited state ligand dissociation in 2 and 3 is believed to be related to the steric hindrance afforded by the presence of two coordinated biq ligands. The ligand exchange quantum yield of 2 is ∼2-fold greater than that of 3, which was shown to be cytotoxic when irradiated with visible light. Cyclometallation results in a red shift of the MLCT absorption maximum of 1 by ∼100 nm relative to those of 2 and 3, but, although 1 exhibits a distorted octahedral geometry, photoinduced ligand exchange does not occur. DFT calculations were used to aid in our understanding of the lack of photochemistry of 1 which is explained by the destabilization of the eg(σ*) orbitals upon cyclometallation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Dedicated to the memory of Prof. Nicholas J. Turro

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...