Total synthesis of macrodiolide ionophores aplasmomycin A and boromycin via double ring contraction†
Abstract
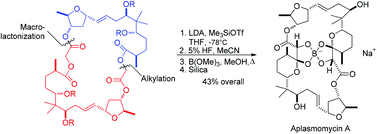
The half structure of the symmetrical macrodiolide aplasmomycin A was synthesized by alkylation of a C3–C10 α-sulfonyl ketone subunit, prepared from (R)-pulegone and protected as a C3 ortholactone with (2R,3R)-butanediol, by a protected 15,16-dihydroxy (12E)-allylic chloride representing C11–C17. The latter was obtained from (2S,3R)-1,2-epoxy-3-butanol and propargyl alcohol. Regio- and stereoselective 5-exo-trig cyclization of the ene diol moiety in this segment, mediated by N-bromosuccinimide, led to the (2R,3S,5R)-tetrahydrofuran substructure of aplasmomycin A. Attachment of an α-acetic ester at the C3 carboxylic acid and esterification of the 3′-hydroxyl group of the tetrahydrofuran as its α-bromoacetate enabled coupling of two aplasmomycin half structures as an α-acyloxy acetate. Mukaiyama macrolactonization of this hydroxy acid afforded a symmetrical 36-membered diolide. Base-mediated double Chan rearrangement of this bis α-acyloxy dilactone caused ring contraction to the 34-membered macrocycle of desboroaplasmomycin A while generating the transannular 2-hydroxy-3-hemiketal motif of the natural product in the correct configuration. Final incorporation of boron into the tetraol core produced aplasmomycin A, isolated as its sodium borate. Extension of this route to the unsymmetrical macrodiolide boromycin was accomplished by modifications that included reversal of C12–C13 olefin geometry to (Z) for the southern half structure along with stereoselective hydride reductions of the C9 ketone that produced (9R) and (9S) alcohols for northern and southern half structures, respectively. Coupling of these half structures was made using an α-acyloxy ester linkage as for aplasmomycin A, but ring closure in this case was orchestrated via a blocked C16 alcohol that left open the C15 hydroxyl group of the southern half for Mukaiyama macrolactonization. A double Chan rearrangement of the resulting 35-membered macrocycle produced the 33-membered diolide of desborodesvalinylboromycin which had been obtained previously by degradation of natural boromycin. Insertion of boron into the tetraol core followed by esterification of the C16 alcohol with a masked D-valine and final deprotection furnished boromycin as its zwitterionic (Böeseken) complex.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...