Anti-cooperative ligand binding and dimerisation in the glycopeptide antibiotic dalbavancin†
Abstract
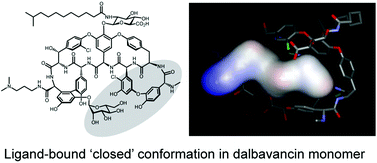
Dalbavancin, a semi-synthetic glycopeptide with enhanced antibiotic activity compared to vancomycin and teicoplanin, binds to the C-terminal lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine subunit of Lipid II, inhibiting peptidoglycan biosynthesis. In this study, micro-calorimetry and electrospray ionization (ESI)-MS have been used to investigate the relationship between oligomerisation of dalbavancin and binding of a Lipid II peptide mimic, diacetyl-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala (Ac2-Kaa). Dalbavancin dimerised strongly in an anti-cooperative manner with ligand-binding, as was the case for ristocetin A, but not for vancomycin and teicoplanin. Dalbavancin and ristocetin A both adopt an ‘closed’ conformation upon ligand binding, suggesting anti-cooperative dimerisation with ligand-binding may be a general feature of dalbavancin/ristocetin A-like glycopeptides. Understanding these effects may provide insight into design of novel dalbavancin derivatives with cooperative ligand-binding and dimerisation characteristics that could enhance antibiotic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...