Development of a PET radiotracer for non-invasive imaging of the reactive oxygen species, superoxide, in vivo†
Abstract
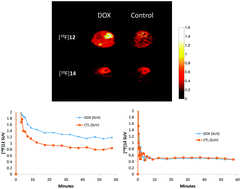
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of a wide range of human disease states and drug toxicities, but development of imaging tools to study ROS biology in vivo remains a challenge. Here we synthesized and validated a novel PET tracer (12) and its 18F radiolabeled version [18F]12 to allow PET (positron emission tomography) imaging of superoxide in vivo. Initial analysis of ROS reaction kinetics found that compound 12 was rapidly and selectively oxidized by superoxide, but not other ROS. Cell culture studies in EMT6 cells exposed to the cancer chemotherapeutic agent Doxorubicin (DOX), which activates the superoxide-generating enzyme, NADPH oxidase, showed that compound 12 was a sensitive and specific probe for superoxide in cells. The microPET imaging of heart in mice with DOX-induced cardiac inflammation observed 2-fold greater oxidation of [18F]12 in the DOX-treated mice compared to controls (p = 0.02), the results were confirmed by distribution studies on organs subsequently removed from the mice and HPLC analysis of [18F] radioactivity compounds. These data indicate that compound 12 is a useful PET tracer to imaging ROS in vivo.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...