Biomimetic aerobic oxidative hydroxylation of arylboronic acids to phenols catalysed by a flavin derivative†
Abstract
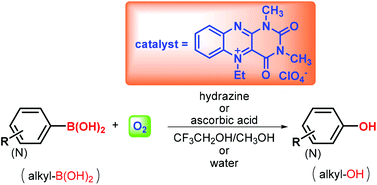
Flavin-catalysed oxidative hydroxylation of substituted arylboronic acids by molecular oxygen with the assistance of hydrazine or ascorbic acid resulted in phenols in high yields. This mild organocatalytic protocol is compatible with a variety of functional groups and it is alternatively usable for transformation of alkylboronic acids to alcohols. Reaction takes place also in water and fulfils criteria for a green procedure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...