Study of Cytochrome c-DNA Interaction – Evaluation of Binding Sites on the Redox Protein†
Abstract
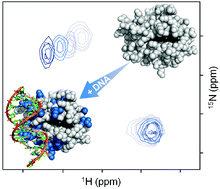
Artificial assemblies consisting of the cationic cytochrome c (cyt c) and double-stranded DNA are interesting for the field of biohybrid systems because of the high electro-activity of the incorporated redox protein. However, little is known about the interactions between these two biomolecules. Here, the complex of reduced cyt c and a 41 base pair oligonucleotide was characterized in solution as a function of pH and ionic strength. Persistent cyt c-DNA agglomerates were observed by UV-vis and DLS (dynamic light scattering) at pH 5.0 and low ionic strength. The strength of the interaction was attenuated by raising the pH or the ionic strength. At pH 7.0 agglomerates were not formed, allowing interaction analysis by NMR spectroscopy. Using TROSY (transverse relaxation-optimized spectroscopy)-HSQC (heteronuclear single quantum coherence) experiments it was possible to identify the DNA binding site on the cyt c surface. Numerous residues surrounding the exposed heme edge of cyt c were involved in transient binding to DNA under these conditions. This result was supported by SEC (size exclusion chromatography) experiments at pH 7.0 showing that the interaction is sufficient for co-elution of cyt c and DNA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...