Magneto-plasmonic nanoparticles as theranostic platforms for magnetic resonance imaging, drug delivery and NIR hyperthermia applications
Abstract
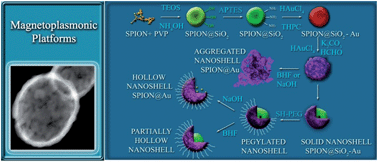
PEGylated magneto-plasmonic nanoparticles with a hollow or semi-hollow interior have been successfully synthesized and their physico-chemical characteristics have been investigated. The hollow interior space can be used to store drugs or other molecules of interest whereas magnetic characterization shows their potential as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) applications. In addition, their plasmonic characteristics in the near infrared (NIR) region make them efficient in photothermal applications producing high temperature gradients after short irradiation times. We show that by controlling the etching conditions the inner silica shell can be selectively dissolved to achieve a hollow or semi-hollow interior without compromising the magnetic or plasmonic characteristics of the resulting nanoparticles. Magnetic measurements and transmission electron microscopy observations have been used to demonstrate the precise control during the etching process and to select an optimal concentration of the etching reagent and contact time to preserve the inner superparamagnetic iron oxide-based nanoparticles and the plasmonic properties of the constructs. Drug loading capabilities were also evaluated for both semi-hollow and as-synthesized nanoparticles using Rhodamine B isothiocyanate as a model compound. The nanoparticles produced could be potentially used as “theranostic” nanoparticles with both imaging capabilities and a dual therapeutic function (drug delivery and hyperthermia).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...