Enhanced radiation therapy with internalized polyelectrolyte modified nanoparticles
Abstract
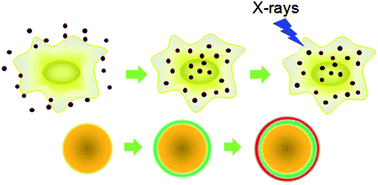
A challenge of X-ray radiation therapy is that high dose X-ray under therapeutic conditions damages normal cells. This paper describes a nanoparticle-based method to enhance X-ray radiation therapy by delivering radio-sensitizing gold nanoparticles into cancer cells. The nanoparticles have been modified with cationic polyelectrolytes to allow internalization. Upon X-ray irradiation of nanoparticles, more photoelectrons and Auger electrons are generated to cause water ionization, leading to formation of free radicals that damage DNA of cancer cells. The X-ray dose required for DNA damage and cell killing is reduced by delivering gold nanoparticles inside cancer cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...