Recombinant antibody mediated delivery of organelle-specific DNA pH sensors along endocytic pathways†
Abstract
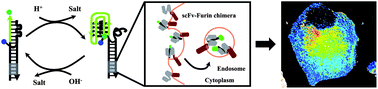
DNA has been used to build nanomachines with potential in cellulo and in vivo applications. However their different in cellulo applications are limited by the lack of generalizable strategies to deliver them to precise intracellular locations. Here we describe a new molecular design of DNA pH sensors with response times that are nearly 20 fold faster. Further, by changing the sequence of the pH sensitive domain of the DNA sensor, we have been able to tune their pH sensitive regimes and create a family of DNA sensors spanning ranges from pH 4 to 7.6. To enable a generalizable targeting methodology, this new sensor design also incorporates a ‘handle’ domain. We have identified, using a phage display screen, a set of three recombinant antibodies (scFv) that bind sequence specifically to the handle domain. Sequence analysis of these antibodies revealed several conserved residues that mediate specific interactions with the cognate DNA duplex. We also found that all three scFvs clustered into different branches indicating that their specificity arises from mutations in key residues. When one of these scFvs is fused to a membrane protein (furin) that traffics via the cell surface, the scFv-furin chimera binds the ‘handle’ and ferries a family of DNA pH sensors along the furin endocytic pathway. Post endocytosis, all DNA nanodevices retain their functionality in cellulo and provide spatiotemporal pH maps of retrogradely trafficking furin inside living cells. This new molecular technology of DNA–scFv–protein chimeras can be used to site-specifically complex DNA nanostructures for bioanalytical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...