Synthesis of active tin: an efficient reagent for allylation reaction of carbonyl compounds†
Abstract
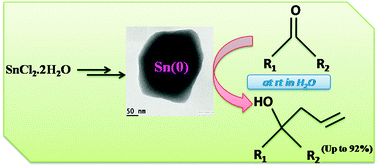
High purity Sn(0) has been obtained as a result of reduction of SnO by sodium stannite (Na2SnO2) in aqueous solution. The process stands unique for the production of tin metal. The as-synthesized tin finds applications in synthetic organic chemistry as a reagent for the allylation of aldehydes and ketones in distilled water at room temperature to give rise to the corresponding homoallylic alcohols with high yield. The reaction occurs without the assistance of heat, ultrasonic vibration, co-solvents/co-reagents, etc. Enhancement of the reaction rate of allylation was observed in water rather than THF. The manipulation of allylation reaction becomes easy with active tin material.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...