Halide-modulated bistate and tristate fluorescence switching for Cu(i) and Ag(i) complexes†
Abstract
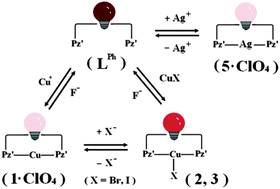
The reaction of a fluorescent trans-chelating ligand LPh (where LPh = 1,3-bis-(3,5-dimethyl-pyrazol-1-ylmethyl)-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine, QY = 9.7%) with MClO4 (M = Cu, Ag) can lead to two-coordinate complexes [M(LPh)](ClO4) (M = Cu (1·ClO4) and Ag (5·ClO4)). When LPh is treated with CuX (X = Cl, Br or I), however, this may lead either to a two-coordinate linear complex [Cu(LPh)](CuCl2) (4·CuCl2) or to three-coordinate T-shaped complexes [Cu(LPh)X] (X = Br (2), I (3)). Moreover, while complex 1·ClO4 shows a ligand substitution for Cl− to form 4·CuCl2, it displays anion coordination for both Br− and I− to give 2 and 3, respectively. All of the copper(I) derivatives can readily liberate ligand LPh upon reacting with F−. As such, a cyclic tristate molecular switching system “LPh ↔ 1·ClO4 ↔ 2 or 3 ↔ LPh” can be accomplished. For complex 5·ClO4, the addition of halides X− (X = Cl, Br, I) results in the abstraction of the silver ions and release of the ligand LPh. A simple “LPh ↔ 5·ClO4” bistate molecular interconversion may also be constructed. Above all, the complexation of either MClO4 or CuX with LPh can be signalled through different quenching effects, QY = 0.5% for 1·ClO4, 3.1% for 2, 3.2% for 3, 0.8% for 4·CuCl2, and 0.3% for 5·ClO4, to realize facile bistate and tristate fluorescence switching operations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...