NH⋯O and OH⋯O interactions of glycine derivatives with squaric acid†
Abstract
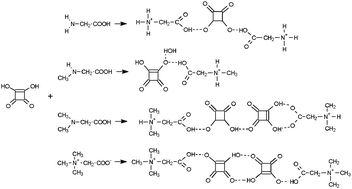
Four new hydrogen-bonded complexes of a simple amino acid glycine (GLY) and its methyl derivatives – sarcosine (N-methylglycine, SAR), dimethylglycine (DMG) and betaine (N,N,N-trimethylglycinium, BET) with squaric acid (3,4-dihydroxy-3-cyclobuten-1,2-dione, H2SQ) are synthesized and characterized by X-ray diffraction, FTIR and NMR spectroscopy. The complexes differ in stoichiometry, interaction with H2SQ and the hydrogen-bonding system. Methylation of glycine gradually reverses the dissociation of squaric acid in co-crystals. This process is correlated with the number of N–H⋯O bonds to the squaric acid oxygens and the N–H donor capability of glycine derivatives. The effect of the presence of methyl groups on the proton and carbon-13 chemical shifts is studied. The DFT calculations are performed for one unit of complexes and stable zwitterionic structures of SAR, DMG and BET in complex with H2SQ, except the GLY unit, are suggested, which appears as an uncharged (neutral) form. The experimental and computed vibrational spectra of complexes studied are reported.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...