Arene ruthenium(ii) complexes induce S-phase arrest in MG-63 cells through stabilization of c-Myc G-quadruplex DNA†
Abstract
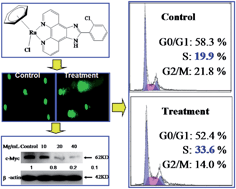
A series of arene ruthenium(II) complexes coordinated by phenanthroimidazole derivatives have been synthesized and evaluated for their in vitro anticancer activities. It has been found that these types of arene Ru(II) complexes, especially [(C6H6)Ru(o-ClPIP)Cl]Cl·2H2O (2a), exhibited acceptable antiproliferative activity against several human cancer cell lines but with low toxicity towards normal HK-2 human cells. Mechanistic studies revealed that 2a-induced growth inhibition against osteosarcoma MG-63 cells was mainly caused by S-phase cell cycle arrest, which was confirmed by the down-regulation of cyclin A and CDK2 using western blot analysis of protein levels. Furthermore, studies using comet assay at single cell level indicated that 2a triggered DNA damage in MG-63 cells, and subsequently initiated S-phase arrest, as shown by the up-regulation of phosphorylated p53 and histone. Moreover, exposure of MG-63 cells to 2a resulted in the down-regulation of c-Myc protein expression. The in vitro DNA-binding behaviors also indicated that 2a could stabilize c-Myc G-quadruplex DNA (G4-DNA) by affecting its conformation. In conclusion, these results suggest that arene Ru(II) complexes coordinated by phenanthroimidazole derivatives serve as c-Myc G4-DNA stabilizers that could induce S-phase arrest in cancer cells by triggering DNA damage, which suggest that these complexes may act as potential candidates for the treatment of human malignant osteosarcoma.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...