Synthesis and biological evaluation of tetrahydropyridinepyrazoles (‘PFPs’) as inhibitors of STAT3 phosphorylation†
Abstract
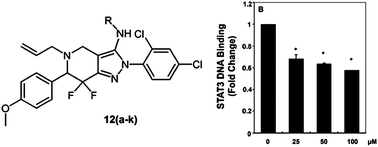
The transcription factor STAT3 is constitutively overexpressed in many human tumors and hence represents a putative target for anticancer drug design. In this work, we describe the synthesis and biological evaluation of a novel chemotype, pyridine-fused pyrazoles (‘PFPs’) as inhibitors of STAT3 phosphorylation. The effect of the compounds synthesized was evaluated in cell proliferation assays of MCF-7 and HepG2 cancer cell lines and two of the compounds tested (12g and 12k) were found to show significant activity. Both compounds were also found to inhibit the proliferation of Hep3B, HUH-7 and PLC/PRF5 HCC cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Furthermore, we established in a DNA binding assay that one of the compounds (12g) was able to significantly inhibit the DNA binding ability of STAT3. Cytotoxicity of 12g against PC3 cells, which do not constitutively phosphorylate STAT3, was found to be minimal, hence lending further support for our mode-of-action hypothesis of this compound. We established for this structure a complete inhibition of CXCL12-induced cell invasion and associated wound healing in HCCLM3 cells, corroborating the proposed modulation of the STAT3 axis by 12g. Finally, molecular modeling was employed to evaluate the hypothesis of PFPs to bind to the SH2 domain of STAT3. Given the efficacy of PFPs in the biological systems studied here we propose their further evaluation in the context of STAT3-mediated cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...