Discovery of selective 2,4-diaminopyrimidine-based photoaffinity probes for glyoxalase I†
Abstract
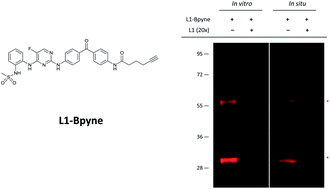
Glyoxalase I (GLO-1) plays a critical role in the detoxification of 2-oxoaldehydes and is highly expressed in cancer cells. Through photo-affinity labelling and affinity pull-down approaches, a series of 2,4-diaminopyrimidine compounds were discovered to selectively bind to GLO-1 in cells. These compounds show potent inhibition of GLO-1 enzyme activity and prevent proliferation of cancer cells. The cell permeable and “clickable” photoaffinity probe L1-Bpyne presented here could be a valuable tool for profiling GLO-1 in live cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...