Changes in the cardiac metabolome caused by perhexiline treatment in a mouse model of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy†
Abstract
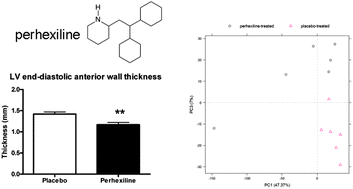
Energy depletion has been highlighted as an important contributor to the pathology of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a common inherited cardiac disease. Pharmacological reversal of energy depletion appears an attractive approach and the use of perhexiline has been proposed as it is thought to shift myocardial metabolism from fatty acid to glucose utilisation, increasing ATP production and myocardial efficiency. We used the Mybpc3–targeted knock-in mouse model of HCM to investigate changes in the cardiac metabolome following perhexiline treatment. Echocardiography indicated that perhexiline induced partial improvement of some, but not all hypertrophic parameters after six weeks. Non-targeted metabolomics, applying ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, described a phenotypic modification of the cardiac metabolome with 272 unique metabolites showing a statistically significant change (p < 0.05). Changes in fatty acids and acyl carnitines indicate altered fatty acid transport into mitochondria, implying reduction in fatty acid beta-oxidation. Increased glucose utilisation is indirectly implied through changes in the glycolytic, glycerol, pentose phosphate, tricarboxylic acid and pantothenate pathways. Depleted reduced glutathione and increased production of NADPH suggest reduction in oxidative stress. These data delineate the metabolic changes occurring during improvement of the HCM phenotype and indicate the requirements for further targeted interventions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...