Investigating correlations in the altered metabolic profiles of obese and diabetic subjects in a South Indian Asian population using an NMR-based metabolomic approach†
Abstract
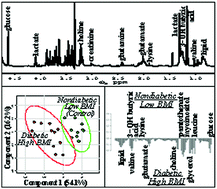
It is well known that obesity/high body mass index (BMI) plays a key role in the evolution of insulin resistance and type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, the exact mechanism underlying its contribution is still not fully understood. This work focuses on an NMR-based metabolomic investigation of the serum profiles of diabetic, obese South Indian Asian subjects. 1H 1D and 2D NMR experiments were performed to profile the altered metabolic patterns of obese diabetic subjects and multivariate statistical methods were used to identify metabolites that contributed significantly to the differences in the samples of four different subject groups: diabetic and non-diabetic with low and high BMIs. Our analysis revealed that the T2DM-high BMI group has higher concentrations of saturated fatty acids, certain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, lysine, proline, threonine, valine, glutamine, phenylalanine, histidine), lactic acid, 3-hydroxybutyric acid, choline, 3,7-dimethyluric acid, pantothenic acid, myoinositol, sorbitol, glycerol, and glucose, as compared to the non-diabetic-low BMI (control) group. Of these 19 identified significant metabolites, the levels of saturated fatty acids, lactate, valine, isoleucine, and phenylalanine are also higher in obese non-diabetic subjects as compared to control subjects, implying that this set of metabolites could be identified as potential biomarkers for the onset of diabetes in subjects with a high BMI. Our work validates the utility of NMR-based metabolomics in conjunction with multivariate statistical analysis to provide insights into the underlying metabolic pathways that are perturbed in diabetic subjects with a high BMI.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...