Plasma metabonomic profiling of lumbar disc herniation and its traditional Chinese medicine subtypes in patients by using gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry†
Abstract
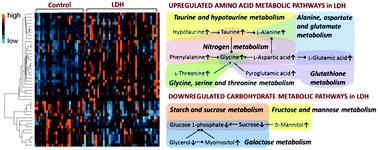
Lumbar disc herniation (LDH) is a commonly occurring disease, threatening human health and life quality. Lack of a gold standard of diagnosis has hindered the efficiency and efficacy of clinical therapy against LDH. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has provided an experience-based but subjective diagnosis system for LDH, demanding objective evidence and explanation. In this study, we adopted a metabonomics approach using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to profile metabolic characteristics of LDH and its TCM subtypes. Plasma samples of 41 LDH patients and 25 healthy controls were collected. LDH patients were classified into two main subtypes, the reality syndrome and deficiency syndrome, according to TCM theory. By using multivariate statistical analysis and metabolism network analysis, we found diverse perturbations of metabolites in amino acid metabolism and carbohydrate metabolism, in which the amino acids (glutamic acid, aspartic acid, glycine, etc.) were up-regulated and a key carbohydrate metabolite (glucose 1-phosphate) was down-regulated. Few differences were found between the two TCM subtypes. Our findings reveal the metabolic disorders of LDH for the first time and demonstrate the feasibility of the metabonomics approach for LDH research but not for its TCM subtypes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...