Structure-based virtual screening of novel, high-affinity BRD4 inhibitors
Abstract
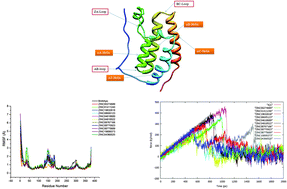
Bromodomains (BRDs) are a diverse family of evolutionarily conserved protein-interaction modules. Among various members of the bromodomain and extra terminal domain family, BRD4 is found to be an important target for many diseases such as cancer, acute myeloid leukemia, multiple myeloma, Burkitt's lymphoma, etc. Therefore, in this study an attempt has been made to screen compounds from NCI Diversity, Drug Bank and Toslab Databases targeting the Kac binding site of BRD4 using molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, MM-PB/GBSA binding free energy calculations and steered molecular dynamics simulations. Using virtual screening and docking, we have identified 11 inhibitors. These new inhibitors exhibit binding energy values higher than that of the (+)JQ1 inhibitor which is effective against BRD4. However, due to the toxicity of (+)JQ1, the designing of new inhibitors becomes significantly important. Thus, these new 11 ligands were systematically analyzed using other computational investigations. Results reveal that the compounds ZINC01411240, ZINC19632618 and ZINC04818522 could be potential drug candidates for targeting BRD4. It can also be seen from the results that there is a linear relationship between the results obtained from the SMD simulation and free energy obtained from the MM-PBSA/GBSA approach. This study clearly illustrates that the steered molecular dynamics can be effectively used for the design of new inhibitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...