Viral proteins that bridge unconnected proteins and components in the human PPI network†
Abstract
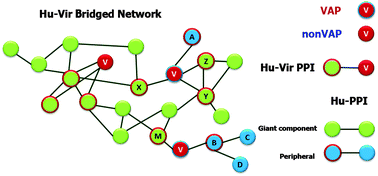
Viruses, despite having small genomes and few proteins, make an array of interactions with host proteins as they solely depend on host machinery for their replication and reproduction. Hence, analysis of the Human–Virus Protein–Protein Interaction Network (Hu–Vir PPI network) helps us to gain certain insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying the hijacking of host cell machinery by viruses for their perpetuation. Here we report an analysis of the Human–Virus Bridged PPI Networks that has led us to identify viral articulation points (VAPs) which connect unconnected components of the Human-PPI (Hu-PPI) network. VAPs cross-link peripheral nodes to the giant component of the Hu-PPI network. VAPs interact with a number of relatively lower topologically central human proteins and are conserved among related viruses. The linked nodes comprise of those that are mostly expressed during viral infection, as well as those that are found exclusively in some metabolic pathways, indicating that the novel viral mediation of certain human protein–protein interactions may form the basis for virus-specific tuning of the host machinery. The functional importance of VAPs and their interaction partners in virus replication make them potential drug targets against viral infection. Our investigations also led to the discovery of an example of a Human Endogenous Retrovirus (HERV) encoded protein, syncytin, as an Articulation Point (AP) in the Hu-PPI network, suggesting that VAPs may be retained in a genome if they result in any beneficial function in the host.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...