Spatiotemporal control of gene expression using microfluidics†
Abstract
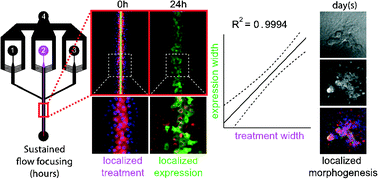
Accurate spatiotemporal regulation of genetic expression and cell microenvironment are both essential to epithelial morphogenesis during development, wound healing and cancer. In vivo, this is achieved through the interplay between intrinsic cellular properties and extrinsic signals. Amongst these, morphogen gradients induce specific concentration- and time-dependent gene expression changes that influence a target cell's fate. As systems biology attempts to understand the complex mechanisms underlying morphogenesis, the lack of experimental setup to recapitulate morphogen-induced patterning in vitro has become limiting. For this reason, we developed a versatile microfluidic-based platform to control the spatiotemporal delivery of chemical gradients to tissues grown in Petri dishes. Using this setup combined with a synthetic inducible gene expression system, we were able to restrict a target gene's expression within a confluent epithelium to bands of cells as narrow as four cell diameters with a one cell diameter accuracy. Applied to the targeted delivery of growth factor gradients to a confluent epithelium, this method further enabled the localized induction of epithelial–mesenchymal transitions and associated morphogenetic changes. Our approach paves the way for replicating in vitro the morphogen gradients observed in vivo to determine the relative contributions of known intrinsic and extrinsic factors in differential tissue patterning, during development and cancer. It could also be readily used to spatiotemporally control cell differentiation in ES/iPS cell cultures for re-engineering of complex tissues. Finally, the reversibility of the microfluidic chip assembly allows for pre- and post-treatment sample manipulations and extends the range of patternable samples to animal explants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...