Hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone by Ni and MoOx co-loaded carbon catalysts
Abstract
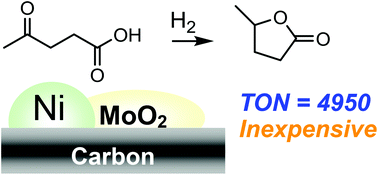
To develop a noble metal-free heterogeneous catalyst for liquid phase hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone under H2, we tested a series of base-metal (Ni, Co, Cu, and Fe) and metal oxides (Mo, V, and W oxides) co-loaded carbon (C) and Ni-loaded metal oxides for the reaction. Ni–MoOx/C pre-reduced at 500 °C showed the highest activity and showed more than 300 times higher turnover number (TON) than previously reported noble metal-free catalysts. A structure–activity relationship study showed that the co-presence of metallic Ni0 species and partially reduced MoO2 could be responsible for the high activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...