Resveratrol and its metabolites inhibit pro-inflammatory effects of lipopolysaccharides in U-937 macrophages in plasma-representative concentrations
Abstract
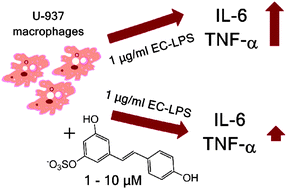
Resveratrol has been shown to exploit various biological activities, including an anti-inflammatory activity. However, resveratrol is metabolized by phase II enzymes post-absorption to predominantly form glucuronides and sulfates. To investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol and its dominating sulfated and glucuronated metabolites formed in vivo, U-937 macrophages were chosen as an immune-competent model system, known to release cytokines upon lipopolysaccharide stimulation. U-937 cells were stimulated with lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli (E. coli-LPS) to evoke an inflammatory reaction, and pre- or co-incubated with 1 or 10 μM of resveratrol (RES), resveratrol-3-sulfate (R3S), resveratrol-disulfates (RDS), resveratrol-3-glucuronide or resveratrol-4′-glucuronide. Time dependent gene expression of IL-6, IL-1α/β and IL-1R by qPCR was studied at 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 9 h, and 24 h of incubation, and the release of IL-6 and TNF-α, after 6 h was analysed by means of non-magnetic or magnetic bead analysis. As a result, 10 μM resveratrol completely inhibited the E. coli-LPS-induced release of IL-6, while resveratrol-3-sulfate and resveratrol-disulfates decreased it by respective 84.2 ± 29.4% and 52.3 ± 39.5%. Whereas TNF-α release was reduced by 48.1 ± 15.4%, 33.0 ± 10.0% and 46.7 ± 8.7% by RES, R3S and RDS, respectively. These results show that not only resveratrol but also resveratrol-3-sulfate and resveratrol-disulfates exhibit an anti-inflammatory potential by counteracting an inflammatory challenge in U-937 macrophages at plasma representative concentrations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...