Bioavailability, distribution and clearance of tracheally instilled, gavaged or injected cerium dioxide nanoparticles and ionic cerium†
Abstract
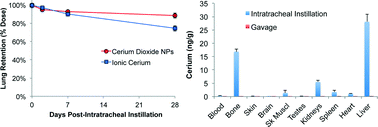
Cerium oxide nanoparticles (NPs) have wide commercial applications. Understanding their fate in the body is fundamental to toxicological evaluations. We compared bioavailability, tissue distribution, clearance and excretion of radioactive 141Ce after intratracheal instillation (IT), gavage, or intravenous (IV) injection of neutron-activated 141CeO2 NPs and 141CeCl3 (ionic 141Ce) in Wistar Han rats. First, we evaluated pulmonary responses to IT-instilled CeO2 NPs and CeCl3 and observed dose-dependent inflammatory effects. Then, groups of rats were IT-instilled with 1 mg kg−1 of 141CeO2 NPs or 0.1 mg kg−1 141CeCl3. Sequential analyses of lungs over 28 days showed slow lung clearance of 141CeO2 NPs (half-life = ~140 days) and of ionic 141Ce (half-life = ~55 days). However, less than 1% and 6% of instilled 141Ce was measured in selected extrapulmonary organs in 141CeO2 NPs and ionic 141Ce groups, respectively. Following gavage (5 mg kg−1), nearly 100% of both test materials was excreted in the feces. Since detected 141Ce activity in tissues could be in nanoparticulate or dissolved form, we also compared the 141Ce tissue distribution post-IV injection with the IT and gavage data. Both IV-injected ionic 141CeCl3 and 141CeO2 NPs were predominantly retained in the liver, bone and spleen, all organs that typically remove circulating particles. We conclude that nanoceria is slowly cleared from the lungs but has minimal extrapulmonary accumulation. Potential risks from prolonged pulmonary retention need further investigation. Risk from ingested nanoceria is likely far lower due to very low absorption and rapid elimination of ceria not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Nanomaterials in air and Nanoceria Research

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...