Inverse spinel NiFeAlO4 as a highly active oxygen evolution electrocatalyst: promotion of activity by a redox-inert metal ion†
Abstract
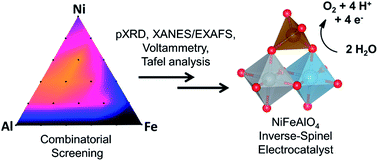
Ni:Fe:Al mixed oxides were identified as highly active water oxidation electrocatalysts. A systematic investigation of these materials has led to the characterization of a well-defined NiFeAlO4 inverse spinel catalyst. Electrochemical characterization of NiFeAlO4 shows activity exceeding previously reported catalysts of similar composition and/or structure, including NiO, NiFe (9 : 1), and NiFe2O4.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...