Dinuclear Mn(ii,ii) complexes: magnetic properties and microwave assisted oxidation of alcohols†
Abstract
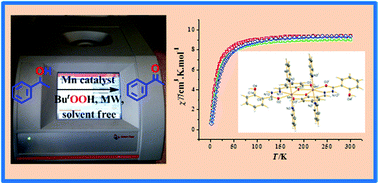
A series of six new mixed-ligand dinuclear Mn(II,II) complexes of three different hydrazone Schiff bases (H3L1, H3L2 and H3L3), derived from condensation of the aromatic acid hydrazides benzohydrazide, 2-aminobenzohydrazide or 2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, with 2,3-dihydroxy benzaldehyde, respectively, is reported. Reactions of Mn(NO3)2·4H2O with the H3L1–3 compounds, in the presence of pyridine (1 : 1 : 1 mole ratio), in methanol at room temperature, yield [Mn(H2L1)(py)(H2O)]2(NO3)2·2H2O (1·2H2O), [Mn(H2L2)(py)(CH3OH)]2(NO3)2·4H2O (2·4H2O) and [Mn(H2L3)(py)(H2O)]2(NO3)2 (3) respectively, whereas the use of excess pyridine yields complexes with two axially coordinated pyridine molecules at each Mn(II) centre, viz. [Mn(H2L1)(py)2]2(NO3)2·H2O (4·H2O), [Mn(H2L2)(py)2]2(NO3)2·2H2O (5·2H2O) and [Mn(H2L3)(py)2]2(NO3)2·2CH3OH (6·2CH3OH), respectively. In all the complexes, the (H2L1–3)− ligand coordinates in the keto form. Complexes 1·2H2O, 2·4H2O, 4·H2O, 5·2H2O and 6·2CH3OH are characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The complexes 1, 2 and 6, having different coordination environments, have been selected for variable temperature magnetic susceptibility measurements to examine the nature of magnetic interaction between magnetically coupled Mn(II) centres and also for exploration of the catalytic activity towards microwave assisted oxidation of alcohols. A yield of 81% (acetophenone) is obtained using a maximum of 0.4% molar ratio of catalyst relative to the substrate in the presence of TEMPO and in aqueous basic solution, under mild conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...