Optical nonlinearities in non-peripherally substituted pyridyloxy phthalocyanines: a combined effect of symmetry, ring-strain and demetallation
Abstract
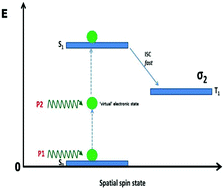
The optical nonlinearities of six non-peripherally-substituted pyridyloxy phthalocyanines have been studied at 532 nm using a nanosecond Z-scan technique in a dimethyl sulphoxide solution. Ring-strain effects and the absence of a metal center were found to greatly reduce the inherent high nonlinearities expected of some of these phthalocyanine complexes. Of the six molecules investigated, 1(4),8(11),15(18),22(25)-tetrakis-(2-pyridyloxy)phthalocyaninato lead(II) 3, 1(4),8(11),15(18),22(25)-tetrakis-(2-pyridyloxy)phthalocyanine 5, and 1(4),8(11),15(18),22(25)-tetrakis-(4-pyridyloxy)phthalocyanine 6 were found to exhibit negligible nonlinear optical behavior, due to either the absence of asymmetry or central metal and/or the presence of a ring-strain effect. A two-photon absorption process was found to be the major contributor to the observed reverse saturable absorption (RSA) in 1(4),8(11),15(18),22(25)-tetrakis-(4-pyridyloxy)phthalocyaninato lead(II) 4, 1(4)-mono-(2-pyridyloxy)phthalocyaninato lead(II) 7, and 1(4)-mono-(4-pyridyloxy)phthalocyaninato lead(II) 8, with large two-photon absorption cross-section, high hyperpolarizability and high third-order susceptibility values in the range of 4.53 × 10−43–5.33 × 10−42 cm4 s per photon, 1.61 × 10−28–1.89 × 10−27 esu and 9.73 × 10−12–7.05 × 10−11 esu respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...