Crystal structure, DFT, spectroscopic and biological activity evaluation of analgin complexes with Co(ii), Ni(ii) and Cu(ii)†
Abstract
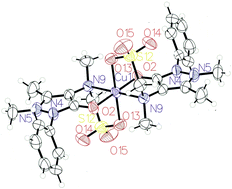
Reaction of analgin (NaL) with Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) salts in ethanol affords complexes of the type [ML2], which were characterized by elemental analysis, FT IR, UV-Vis, EPR, TG/DTA, magnetic susceptibility and conductance measurements. The copper(II) complex crystallizes in the orthorhombic Pbca space group. Analgin behaves as a mono-negatively tridentate ligand via pyrazolone O, sulfonate O and tertiary amino groups. The interaction of the tertiary nitrogen with Mn+ ions is the main factor which determines the stability of complexes as revealed from natural bond orbital analysis data, where the binding energy of [ML2] decreases with an increase in the bond length of the M–N bond. Time-dependent density functional theory calculations were applied in order to realize the electronic structures and to explain the related experimental observations. The anti-bacterial activity was studied on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Coordination of analgin to Ni(II) and Cu(II) leads to a significant increase in its antibacterial activity as compared with the Co(II) complex.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...