One-step fabrication of functionalized magnetic adsorbents with large surface area and their adsorption for dye and heavy metal ions†
Abstract
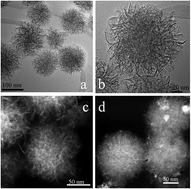
Functionalized magnetic adsorbents (FMAs) were synthesized by a facile and surfactant-free one-pot solvothermal approach, using iron(III) chloride hexahydrate as the precursor, ethylene glycol as the reducing agent, ammonium acetate, and EDTA-2Na as an electrostatic stabilization agent. The self-assembly process of the functionalized magnetic adsorbents has been investigated and a plausible mechanism is proposed. The resulting functionalized magnetic adsorbents have relatively high specific surface areas (71.6 m2 g−1), excellent magnetic properties and rich functional groups (carboxyl groups, hydroxyl groups and hydrophobic groups). Meanwhile, the resulting FMAs were employed in the adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Herein, we took two types of typical pollutants, dyes (methylene blue (MB) and malachite green (MG)) and toxic heavy metal ions (Cr(VI) and Pb(II)) as examples of organic and inorganic pollutants in environmental water. The excellent intrinsic properties of the FMAs led to a stronger adsorption ability than a solid Fe3O4 adsorbent for MB, MG, Cr(VI) and Pb(II). Especially, the simultaneous adsorption of the functionalized flower-like magnetic adsorbents for MG and Pb(II) was also determined in a binary system. Finally, it was demonstrated that the resulting flower-like magnetic adsorbents are expected to be a good candidate as an adsorbent for water treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...