Zinc(ii) and cadmium(ii) metal–organic frameworks with 4-imidazole containing tripodal ligand: sorption and anion exchange properties†
Abstract
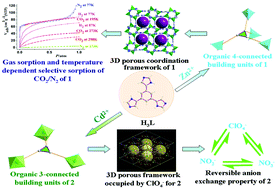
The use of a 4-imidazole containing tripodal ligand 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-4-yl)benzene (H3L) enabled isolation of two three-dimensional (3D) porous metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) [Zn(HL)]·solvent (1) and [Cd(H3L)2](ClO4)2·10.5H2O (2) featuring 4,4- and 3,6-connected nets related to the structures of ecl and pyrite, respectively. Framework 1 has 3D channels based on Zn–Im− (Im− = imidazolate) moieties due to partial deprotonation of the 1H-imidazol-4-yl groups of H3L while porous framework 2 is constructed by the coordination of neutral H3L ligands with Cd(II). Desolvated solid 1′ showed remarkable uptake for CO2, N2, H2, CH4 gases as well as the volatile organic vapor of MeOH, EtOH, i-PrOH and C6H6, significantly, exhibiting temperature dependent selective gas sorption for CO2 over N2. Grand Canonical Monte Carlo (GCMC) simulations were performed to elucidate the mechanism of the selective gas adsorption. Cage-like motifs are found in pyrite-net 2, in which ClO4− anions are hosted, and the results of IR, elemental analysis and PXRD measurements confirm that 2 has a reversible anion exchange property among perchlorate, nitrate and nitrite anions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...