H6phospa-trastuzumab: bifunctional methylenephosphonate-based chelator with 89Zr, 111In and 177Lu†
Abstract
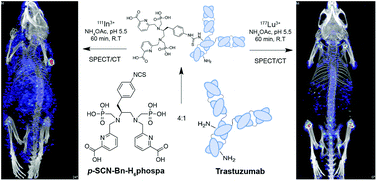
The acyclic chelator H6phospa and the bifunctional derivative p-SCN–Bn–H6phospa have been synthesized using nosyl protection chemistry and evaluated with 89Zr, 111In, and 177Lu. The p-SCN–Bn–H6phospa derivative was successfully conjugated to trastuzumab with isotopic dilution assays indicating 3.3 ± 0.1 chelates per antibody and in vitro cellular binding assays indicating an immunoreactivity value of 97.9 ± 2.6%. Radiolabeling of the H6phospa-trastuzumab immunoconjugate was achieved with 111In in 70–90% yields at room temperature in 30 minutes, while 177Lu under the same conditions produced more inconsistent yields of 40–80%. Stability experiments in human serum revealed the 111In-phospa-trastuzumab complex to be 52.0 ± 5.3% intact after 5 days at 37 °C, while the 177Lu-phospa-trastuzumab to be only 2.0 ± 0.3% intact. Small animal SPECT/CT imaging using mice bearing subcutaneous SKOV-3 ovarian cancer xenografts was performed, and it was found that 111In-phospa-trastuzumab successfully identified and delineated small (∼2 mm in diameter) tumors from surrounding tissues, despite visible uptake in the kidneys and bone due to moderate chelate instability. As predicted from stability assays in serum, the 177Lu-phospa-trastuzumab conjugate served as a negative control and displayed no tumor uptake, with high uptake in bones indicating rapid and complete radiometal dissociation and suggesting a potential application of H6phospa in transient lanthanide chelation for bone-delivery. Radiolabeling with 89Zr was attempted, but even with elevated temperatures of 37 °C, the maximum observed radiometal incorporation over 18 hours was 12%. It can be concluded from this work that H6phospa is not superior to the previously studied H4octapa for use with 111In and 177Lu, but improvements in 89Zr radiolabeling were observed over H4octapa, suggesting H6phospa to be an excellent starting point for elaboration of 89Zr-based radiopharmaceutical development. To our knowledge, H6phospa is the best desferrioxamine alternative for 89Zr radiolabeling to be studied to date.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...