Efficient H2 generation from formic acid using azole complexes in water†
Abstract
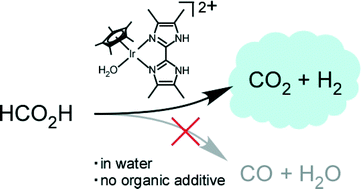
Iridium azole-containing complexes are demonstrated to catalyze the dehydrogenation of formic acid into H2–CO2 (1/1) mixtures in aqueous solution in the absence of organic additives, and with a maximum turnover frequency (TOF) of 34 000 h−1 at 80 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...