Heterolytic cleavage of Si–H bonds: reduction of imines using silane/high-valent oxo-molybdenum MoO2Cl2 as a catalyst†
Abstract
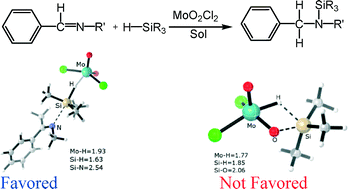
This work describes a DFT investigation into reducing imines using a high-valent MoO2Cl2/silane system, proposing that a recently introduced mechanistic model, the heterolytic Si–H bond cleavage upon imine substrates attacking the η1-silane molybdenum adduct, accounts for this catalytic reactivity, rather than the [2 + 2] addition mechanism.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...