Optimization of absorption bands of dye-sensitized and perovskite tandem solar cells based on loss-in-potential values†
Abstract
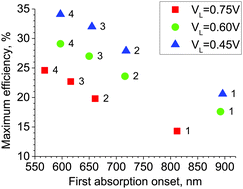
A numerical study of optimal bandgaps of light absorbers in tandem solar cell configurations is presented with the main focus on dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) and perovskite solar cells (PSCs). The limits in efficiency and the expected improvements of tandem structures are investigated as a function of total loss-in-potential (VL), incident photon to current efficiency (IPCE) and fill factor (FF) of individual components. It is shown that the optimal absorption onsets are significantly smaller than those derived for multi-junction devices. For example, for double-cell devices the onsets are at around 660 nm and 930 nm for DSSCs with iodide based electrolytes and at around 720 nm and 1100 nm for both DSSCs with cobalt based electrolytes and PSCs. Such configurations can increase the total sunlight conversion efficiency by about 35% in comparison to single-cell devices of the same VL, IPCE and FF. The relevance of such studies for tandem n–p DSSCs and for a proposed new configuration for PSCs is discussed. In particular, it is shown that maximum total losses of 1.7 V for DSSCs and 1.4 V for tandem PSCs are necessary to give any efficiency improvement with respect to the single bandgap device. This means, for example, a tandem n–p DSSC with TiO2 and NiO porous electrodes will hardly work better than the champion single DSSC. A source code of the program used for calculations is also provided.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...