Interactions of adsorbed CO2 on water ice at low temperatures
Abstract
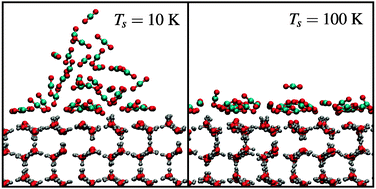
We present a computational study into the adsorption properties of CO2 on amorphous and crystalline water surfaces under astrophysically relevant conditions. Water and carbon dioxide are two of the most dominant species in the icy mantles of interstellar dust grains and a thorough understanding of their solid phase interactions at low temperatures is crucial for understanding the structural evolution of the ices due to thermal segregation. In this paper, a new H2O–CO2 interaction potential is proposed and used to model the ballistic deposition of CO2 layers on water ice surfaces, and to study the individual binding sites at low coverages. Contrary to recent experimental results, we do not observe CO2 island formation on any type of water substrate. Additionally, density functional theory calculations are performed to assess the importance of induced electrostatic interactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...