Physicochemical properties of pentaglyme–sodium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide solvate ionic liquid†
Abstract
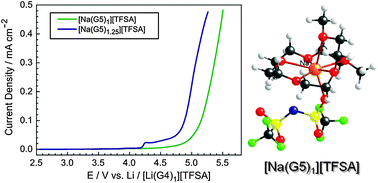
The physicochemical properties of pentaglyme (G5) and sodium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide (Na[TFSA]) binary mixtures were investigated with respect to salt concentration and temperature. The density, viscosity, ionic conductivity, self-diffusion coefficient, and oxidative stability of a series of binary mixtures were measured, and the mixtures were examined as electrolytes for Na secondary batteries. An equimolar mixture of G5 and Na[TFSA] formed a low melting solvate, [Na(G5)1][TFSA], which exhibited an ionic conductivity of 0.61 mS cm−1 at 30 °C. The ionicity (Λimp/Λideal) of the glyme–Na[TFSA] mixture was estimated from the molar conductivity of electrochemical impedance measurements (Λimp) and the Walden plot (Λideal). [Na(G5)1][TFSA] possessed a high ionicity of 0.63 at 30 °C, suggesting that [Na(G5)1][TFSA] is highly dissociated into a [Na(G5)1]+ cation and a [TFSA]− anion, regardless of the extreme salt concentration in the liquid. The oxidative stabilities of G5–Na[TFSA] mixtures were investigated by linear sweep voltammetry, and the higher concentration resulted in higher oxidative stability due to the lowering of the HOMO energy level of G5 by complexation with the Na+ ion. In addition, battery tests were performed using the mixtures as electrolytes. The [Na|[Na(G5)1][TFSA]|Na0.44MnO2] cell showed good charge–discharge cycle stability, with a discharge capacity of ca. 100 mA h g−1, while the [Na(G5)1.25][TFSA] system, containing excess G5, showed poor stability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...