Human serum albumin binding to silica nanoparticles – effect of protein fatty acid ligand†
Abstract
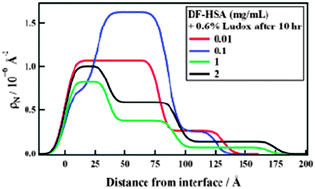
Neutron reflectivity shows that fatted (F-HSA) and defatted (DF-HSA) versions of human serum albumin behave differently in their interaction with silica nanoparticles premixed in buffer solutions although these proteins have close to the same surface excess when the silica is absent. In both cases a silica containing film is quickly established at the air–water interface. This film is stable for F-HSA at all relative protein–silica concentrations measured. This behaviour has been verified for two small silica nanoparticle radii (42 Å and 48 Å). Contrast variation and co-refinement have been used to find the film composition for the F-HSA–silica system. The film structure changes with protein concentration only for the DF-HSA–silica system. The different behaviour of the two proteins is interpreted as a combination of three factors: increased structural stability of F-HSA induced by the fatty acid ligand, differences in the electrostatic interactions, and the higher propensity of defatted albumin to self-aggregate. The interfacial structures of the proteins alone in buffer are also reported and discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: PCCP’s 15th anniversary

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...