Driving charge separation for hybrid solar cells: photo-induced hole transfer in conjugated copolymer and semiconductor nanoparticle assemblies†
Abstract
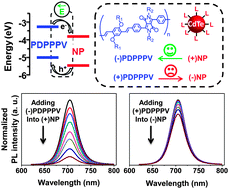
This work reports on the use of an internal electrostatic field to facilitate charge separation at inorganic–organic interfaces, analogous to those in hybrid solar cells. Systematic charge transfer studies show that the donor–acceptor charge transfer rate is highly sensitive to the direction of the internal electric field.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...