Effect of in situ synthesized Fe2O3 and Co3O4 nanoparticles on electroactive β phase crystallization and dielectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) thin films
Abstract
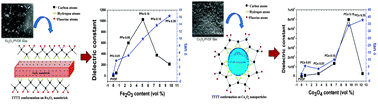
A simple and low cost in situ process has been developed to synthesize Fe2O3–Co3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) loaded poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) thin films. The electroactive β phase nucleation mechanism and the dielectric properties of the films have been investigated by X-ray diffraction spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry and using an LCR meter. Results confirmed that the electroactive β phase crystallization in the PVDF matrix is due to the fast nucleating or catalytic effect of the in situ NPs. Homogenous dispersion of in situ Fe2O3–Co3O4 NPs in the polymer matrix leads to strong interfacial interaction between the NPs and the polymer resulting in enhanced β phase nucleation in PVDF and a large dielectric constant of the thin films. The observed variation in the electroactive β phase nucleation by NPs (Fe2O3–Co3O4) and the dielectric properties of the thin films have been explained on the basis of surface charge, size, geometrical shape and extent of agglomeration of the NPs in the polymer matrix.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...