Orientation- and passivation-dependent stability and electronic properties of α-Si3N4 nanobelts
Abstract
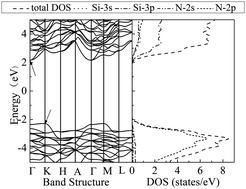
The energetic stability and electronic properties of unpassivated, hydrogen (–H) and hydroxyl (–OH) passivated α-Si3N4 nanobelts orientating along the [101], [210], [011], [100], [001], and [110] directions are investigated by first-principles calculations. Calculations show that the energetic stabilities of α-Si3N4 nanobelts depend weakly upon orientations of nanobelts, but sensitively on passivation treatments. The most stable nanobelt is the OH cluster partially passivated α-Si3N4, followed by the H atom fully passivated and the unpassivated systems. All the unpassivated nanobelts show metallic characteristics due to the presence of dangling bonds of surficial atoms in nanobelts, while all the passivated nanobelts exhibit semiconducting characteristics. The valence band maximum (VBM) and the conduction band minimum (CBM) mainly originate from the surface N-2p and Si-3p states, respectively. For α-Si3N4 nanobelts orientating along [101], [210], [011] and [110] directions, the OH passivated systems exhibit a much smaller band gap than the H passivated systems, while the [100] and [001] orientated nanobelts exhibit the opposite band-gap properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...