The strength and directionality of a halogen bond are co-determined by the magnitude and size of the σ-hole
Abstract
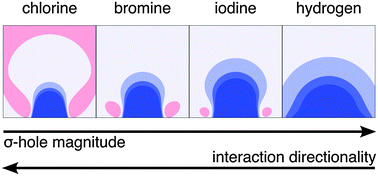
The σ-holes of halogen atoms on various aromatic scaffolds were described in terms of their size and magnitude. The electrostatic potential maps at the CAM-B3LYP-D3(bj)/def2-QZVP level were calculated and the σ-holes of more than 100 aromatic analogues were thoroughly analysed to relate the σ-holes to the binding preferences of the halogenated compounds. Both the size and magnitude of the σ-hole increase when passing from chlorinated to iodinated analogues. Also, the σ-hole properties were studied upon chemical substitution of the aromatic ring as well as in the aromatic ring. Further, the angular variations of the interactions were investigated on a selected set of halogenbenzene complexes with argon and hydrogen fluoride (HF). In order to analyse interaction energy components, DFT-SAPT angular scans were performed. The interaction energies of bromobenzene complexes were evaluated at the CCSD(T)/complete basis set level providing the benchmark energetic data. The strength of the halogen bond between halogenbenzenes and Ar atoms and HF molecules increases while its directionality decreases when passing from chlorine to iodine. The decrease of the directionality of the halogen bond is larger for a HF-containing complex and is caused by electrostatic and exchange-repulsion energies. These findings are especially valuable for protein-halogenated ligand-binding studies, applied in the realm of rational drug development and lead optimisation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: PCCP’s 15th anniversary

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...