DFT analysis of Li intercalation mechanisms in the Fe-phthalocyanine cathode of Li-ion batteries†
Abstract
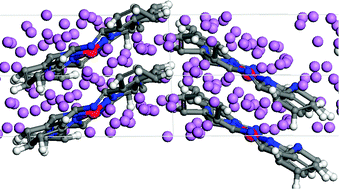
New materials with high intercalation capacity are needed for cathodic materials in order to overcome small capacities at high discharge rates in Li-ion batteries. High intercalation capacities have been reported in the experimental setup using iron phthalocyanine (FePc) as cathodic material; however the real intercalation capacity and the chemistry occurring during the intercalation process are still being debated. In this work we analyze the intercalation of Li atoms in FePc periodic structures using density functional theory including a semi-empirical approach to represent van der Waals (vdW) forces. Within this approach we find intercalation capacities of about 20 Li atoms per FePc molecule at a discharge voltage of ∼0.5 V (with respect to Li/Li+), and up to 37 Li atoms at lower voltages. The intercalation process is driven mainly by electrostatic interactions between positively charged Li ions and negatively charged FePc molecules, with vdW interactions playing an essential role in reaching the high number of intercalated Li atoms. The reduction of the central Fe atom leading to charges evolving from +1.2 to −0.2 is responsible for the high intercalation voltage; however the further reduction contributions of N, C, and even H atoms make FePc a suitable cathode for Li-ion battery applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...